Kelly Warner Law Firm Blames USA Herald for Arizona Bar Investigation
5/17/17 Based on the information released in The Washington Post article on 5/17/17, the USA Herald publishes another in-depth article that…
By – USA HeraldAaron Kelly Law Firm Resorts To Attacking Former Client Again On KellyWarnerLaw.com – Pattern Recognized
Professor Volokh thereafter filed a bar complaint against Dan Warner with the Arizona Bar. This eventually led the ABA to…
By – Jeff WattersonArizona Bar Opens Investigation on Attorney Aaron Kelly
USA Herald recently reported on a developing story involving Attorneys Daniel Warner and Aaron Kelly. Both Warner and Kelly have…
By – Paul O'NealParamount President PR $150M Lawsuit Sparks Explosive Allegations
Meeting Ends Without Deal According to the complaint, Cipriani and Shell met Feb. 2 at a lawyer’s office in an…
By – Rachel MooreSpaceX’s Starship V3 Test Delayed as NASA Pushes Faster Lunar Lander Development
NASA Urges Faster Progress for Artemis While SpaceX fine-tunes its next launch, pressure is mounting from NASA, which is relying…
By – Rachel MooreAR-15 Rihanna Home Attack: Armed Suspect Fires Shots at Singer’s Beverly Hills Residence
Suspect’s Criminal History Records reviewed by The Times show Ortiz has had several encounters with law enforcement in her home…
By – Rachel MooreLive Nation DOJ Antitrust Fight Settlement Ends High-Stakes Court Battle
Amphitheater Divestitures Ordered The settlement also tackles Live Nation’s powerful foothold in the amphitheater market. According to federal officials, the…
By – Rachel MoorePentagon-Anthropic AI Dispute Explodes Into Federal Lawsuits Over AI Safety Policies
A Rare and Controversial Blacklist National security experts say the government’s designation is highly unusual. Supply-chain risk labels are typically…
By – Rachel MooreG7 Oil Reserve Release Considered as Iran War Disrupts Global Energy Supply
A Historic Supply Shock According to analysts at consulting firm Rapidan Energy Group, the closure of the strait has triggered…
By – Rihem AkkoucheParamount President PR $150M Lawsuit Sparks Explosive Allegations
Meeting Ends Without Deal According to the complaint, Cipriani and Shell met Feb. 2 at a lawyer’s office in an…
By – Rachel MooreSpaceX’s Starship V3 Test Delayed as NASA Pushes Faster Lunar Lander Development
NASA Urges Faster Progress for Artemis While SpaceX fine-tunes its next launch, pressure is mounting from NASA, which is relying…
By – Rachel MooreAR-15 Rihanna Home Attack: Armed Suspect Fires Shots at Singer’s Beverly Hills Residence
Suspect’s Criminal History Records reviewed by The Times show Ortiz has had several encounters with law enforcement in her home…
By – Rachel MooreLive Nation DOJ Antitrust Fight Settlement Ends High-Stakes Court Battle
Amphitheater Divestitures Ordered The settlement also tackles Live Nation’s powerful foothold in the amphitheater market. According to federal officials, the…
By – Rachel MoorePentagon-Anthropic AI Dispute Explodes Into Federal Lawsuits Over AI Safety Policies
A Rare and Controversial Blacklist National security experts say the government’s designation is highly unusual. Supply-chain risk labels are typically…
By – Rachel MooreG7 Oil Reserve Release Considered as Iran War Disrupts Global Energy Supply
A Historic Supply Shock According to analysts at consulting firm Rapidan Energy Group, the closure of the strait has triggered…
By – Rihem AkkoucheParamount President PR $150M Lawsuit Sparks Explosive Allegations
Meeting Ends Without Deal According to the complaint, Cipriani and Shell met Feb. 2 at a lawyer’s office in an…
By – Rachel MooreSpaceX’s Starship V3 Test Delayed as NASA Pushes Faster Lunar Lander Development
NASA Urges Faster Progress for Artemis While SpaceX fine-tunes its next launch, pressure is mounting from NASA, which is relying…
By – Rachel MooreAR-15 Rihanna Home Attack: Armed Suspect Fires Shots at Singer’s Beverly Hills Residence
Suspect’s Criminal History Records reviewed by The Times show Ortiz has had several encounters with law enforcement in her home…
By – Rachel MooreLive Nation DOJ Antitrust Fight Settlement Ends High-Stakes Court Battle
Amphitheater Divestitures Ordered The settlement also tackles Live Nation’s powerful foothold in the amphitheater market. According to federal officials, the…
By – Rachel MoorePentagon-Anthropic AI Dispute Explodes Into Federal Lawsuits Over AI Safety Policies
A Rare and Controversial Blacklist National security experts say the government’s designation is highly unusual. Supply-chain risk labels are typically…
By – Rachel MooreG7 Oil Reserve Release Considered as Iran War Disrupts Global Energy Supply
A Historic Supply Shock According to analysts at consulting firm Rapidan Energy Group, the closure of the strait has triggered…
By – Rihem AkkoucheThe Northern Lights Return
The Northern Lights have a chance to be visible from several northern U.S. states on Tuesday night, forecasters at the…
By – Jackie AllenFebruary Unemployment Up as Job Losses Surprise Economists
According to the BLS: Producer prices rose 2.9% year-over-year through January 2026 Core PPI increased 3.6%, excluding food and energy…
By – Jackie AllenLate-Night Attack by Venezuelan National at Florida Beach
Officials noted that the suspect had overstayed his work visa at the time of the attack. For more details on…
By – Jackie AllenTrump’s War in Iran: Congress Confronts Escalation After U.S. Strikes
On the Republican side, most lawmakers appear to back Trump’s strategy. Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Ark.), chair of the Senate Intelligence…
By – Jackie AllenU.S. And Israel Launch Major Strikes On Iran — What It Means For America
Continuation of military strikes if Iran persists in retaliatory attacks. Diplomacy or ceasefire negotiations if international pressure increases. A broader…
By – Samuel LopezU.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit Overturns $8M Asbestos Verdict Against BNSF Railway Co.
BNSF declined to comment on the decision. Judges Consuelo M. Callahan, Morgan B. Christen and Andrew D. Hurwitz sat on…
By – Tyler BrooksParamount President PR $150M Lawsuit Sparks Explosive Allegations
Meeting Ends Without Deal According to the complaint, Cipriani and Shell met Feb. 2 at a lawyer’s office in an…
By – Rachel MooreSpaceX’s Starship V3 Test Delayed as NASA Pushes Faster Lunar Lander Development
NASA Urges Faster Progress for Artemis While SpaceX fine-tunes its next launch, pressure is mounting from NASA, which is relying…
By – Rachel MooreAR-15 Rihanna Home Attack: Armed Suspect Fires Shots at Singer’s Beverly Hills Residence
Suspect’s Criminal History Records reviewed by The Times show Ortiz has had several encounters with law enforcement in her home…
By – Rachel MooreLive Nation DOJ Antitrust Fight Settlement Ends High-Stakes Court Battle
Amphitheater Divestitures Ordered The settlement also tackles Live Nation’s powerful foothold in the amphitheater market. According to federal officials, the…
By – Rachel MoorePentagon-Anthropic AI Dispute Explodes Into Federal Lawsuits Over AI Safety Policies
A Rare and Controversial Blacklist National security experts say the government’s designation is highly unusual. Supply-chain risk labels are typically…
By – Rachel MooreG7 Oil Reserve Release Considered as Iran War Disrupts Global Energy Supply
A Historic Supply Shock According to analysts at consulting firm Rapidan Energy Group, the closure of the strait has triggered…
By – Rihem AkkoucheWhen The Files Are Finally Unsealed The Most Mind-Bending Truth May Not Be What We Expect
[USA HERALD] – There is a widespread assumption that if governments release their most highly classified files related to unidentified…
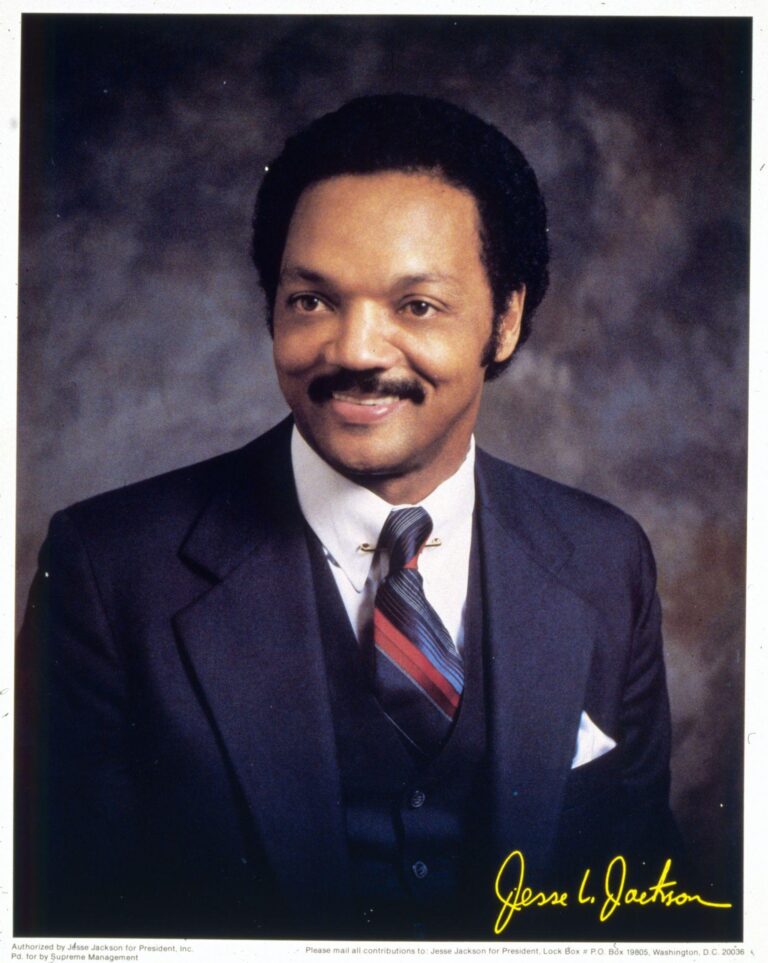
By – Samuel LopezCivil Rights Icon Rev. Jesse Jackson Dies at 84 As President Trump Issues Personal Tribute
Even in later years, as illness softened his voice and slowed his step, Jackson remained active. In 2021, he was…
By – Samuel LopezClues to Savannah Guthrie Missing Mom’s Disappearance Found on Security System
Community Support Grows as Search Continues As the investigation intensifies, the local community has rallied around the family. Neighbors and…
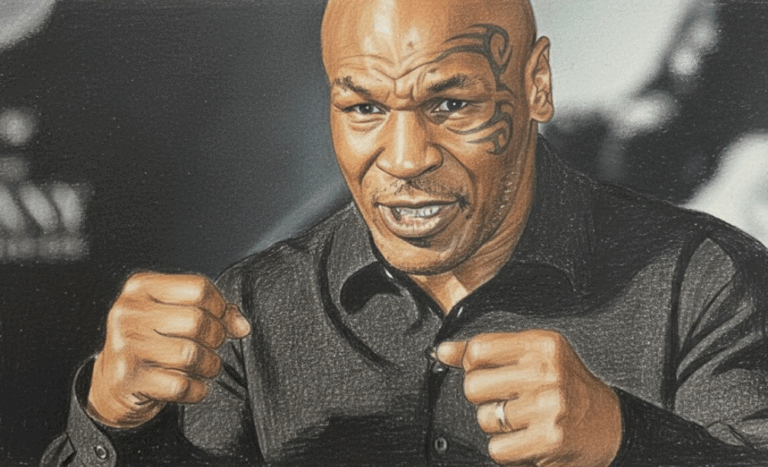
By – Jackie AllenMike Tyson Urges Americans to ‘Eat Real Food’ in Emotional Super Bowl Ad Highlighting Health Risks
Boxing legend Mike Tyson is using his platform ahead of Super Bowl 60 to address a personal and national health…
By – Tyler BrooksDeadly “Death Cap” Mushrooms in California Cause Multiple Deaths and Liver Transplants Amid Rare Super Bloom
California health officials are warning the public after four deaths and three liver transplants linked to the highly toxic death…
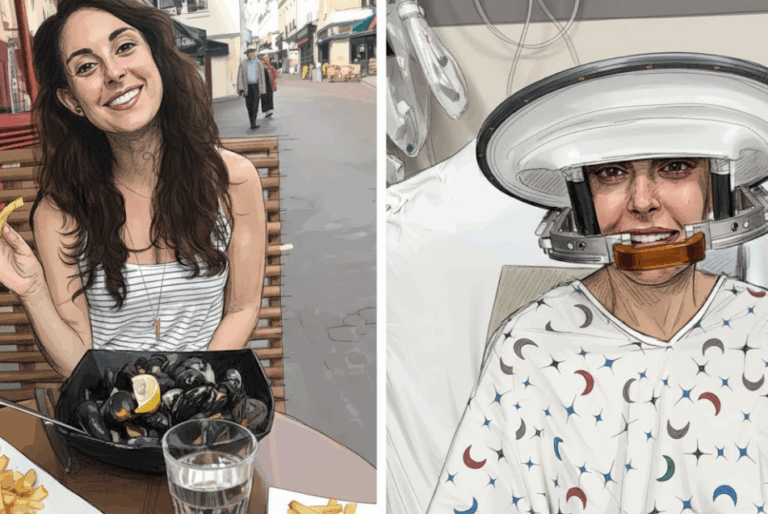
By – Ahmed BoughallebFrom Migraines to Miracles: How Becca Valle Survived a Glioblastoma Diagnosis Against the Odds
Becca Valle, 41, thought her headaches were just migraines—until a sudden, unbearable pain revealed something far more serious. In September…
By – Tyler BrooksFebruary Unemployment Up as Job Losses Surprise Economists
According to the BLS: Producer prices rose 2.9% year-over-year through January 2026 Core PPI increased 3.6%, excluding food and energy…
By – Jackie AllenLate-Night Attack by Venezuelan National at Florida Beach
Officials noted that the suspect had overstayed his work visa at the time of the attack. For more details on…
By – Jackie AllenTrump’s War in Iran: Congress Confronts Escalation After U.S. Strikes
On the Republican side, most lawmakers appear to back Trump’s strategy. Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Ark.), chair of the Senate Intelligence…
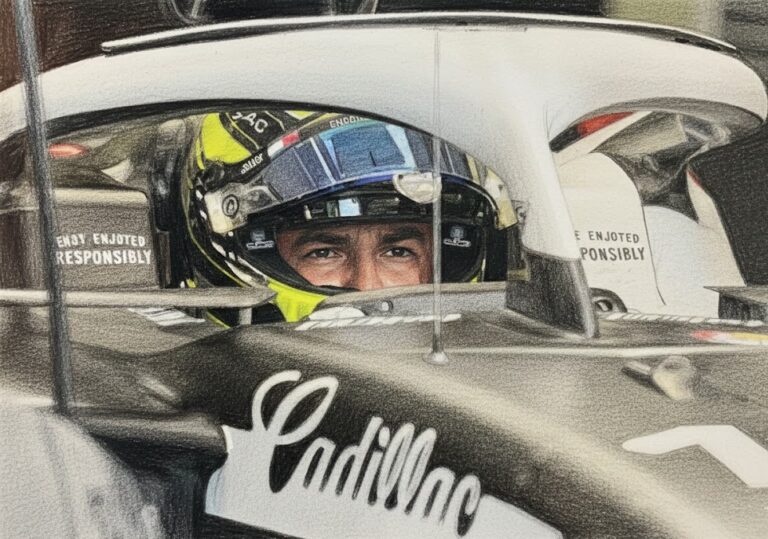
By – Jackie AllenCadillac Names Inaugural Formula 1 Car MAC-26 in Tribute to Mario Andretti Ahead of 2026 Australian Grand Prix Debut
Lowdon has previously spoken about Andretti’s early encouragement during the team’s formation stages, noting that the racing legend asked him…
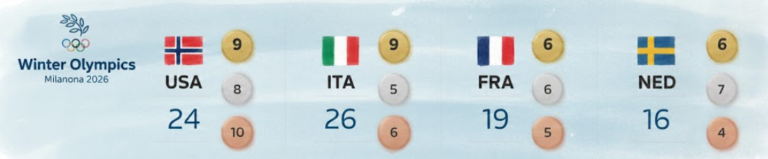
By – Ahmed BoughallebNorway Tops Medal Table After Day 13 at 2026 Winter Olympics as Team USA Surges Into Second Place
With 13 days complete at the 2026 Milan Cortina Winter Olympics, Norway sits atop the overall medal standings, collecting 34…
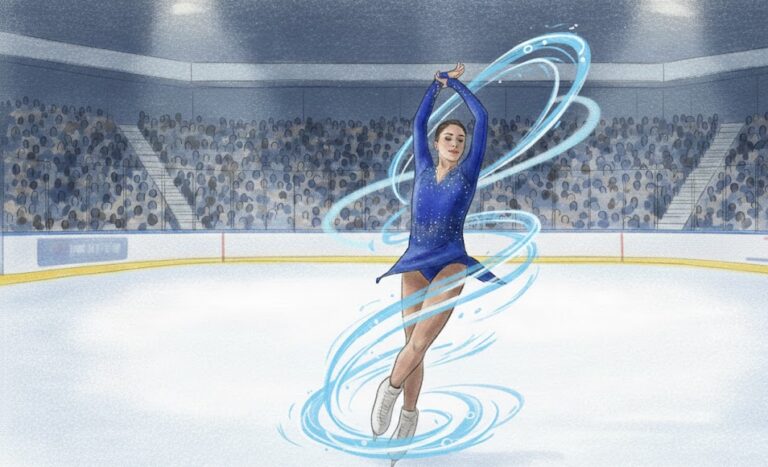
By – Ahmed BoughallebOlympic Science Explained: How Figure Skaters Spin at Blinding Speeds Without Getting Dizzy
When Amber Glenn finishes her routine, the arena usually rises with her. The music builds, her blades carve a tight…
By – Tyler BrooksNo posts found.
No posts found.
 No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!