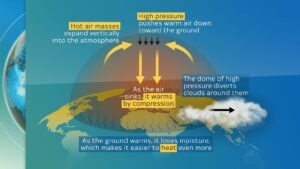
The heat dome acts like a pressure lid, trapping hot air beneath it and facilitating the formation of heatwaves marked by temperatures significantly higher than the norm.
The mechanism behind a heat dome involves hot air expanding vertically into the atmosphere. The pressure from above confines this warm air, pushing it downward.
As the warm air sinks, it compresses and further heats up, intensifying the heat buildup. This process leads to increased ground temperatures and decreased moisture levels, creating conditions ripe for wildfires.
The high-pressure system of the dome influences cloud movement, further contributing to the heat retention.
Widespread Impact
While Texas has been the epicenter of extreme heat this summer, its effects have rippled across the country, reaching as far east as Florida and as far west as interior Southern California.
The central and northern Plains, along with parts of the Midwest, are poised to experience the most sweltering temperatures of 2023 as the heat surge intensifies over the upcoming weekend and into the following week.


