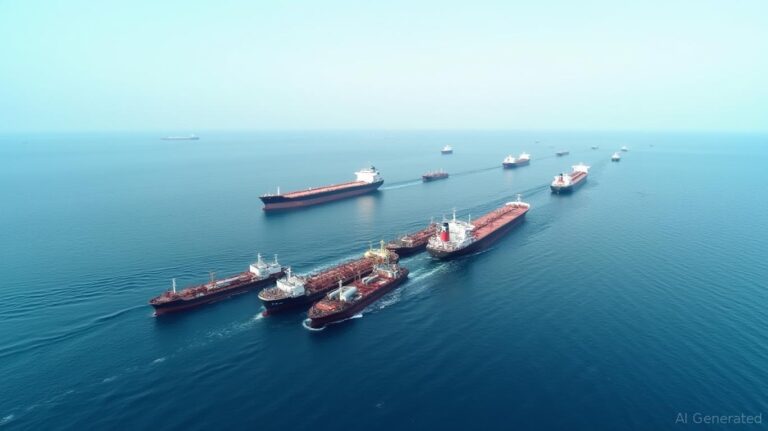
Hormuz Shock Hits U.S. Legal And Insurance Sectors As War Risk, Cargo Claims And Contract Fights Begin to Spread
The legal sector impact is just as significant, and in some ways more underreported. What experienced coverage lawyers and commercial…
By – Samuel LopezBeyond Gas Prices The Strait of Hormuz Crisis Could Hit Fertilizer, Plastics, Aluminum And Global Supply Chains
Plastics and petrochemicals are another underappreciated vulnerability. Middle Eastern producers ship enormous volumes of chemicals and plastics through this route,…
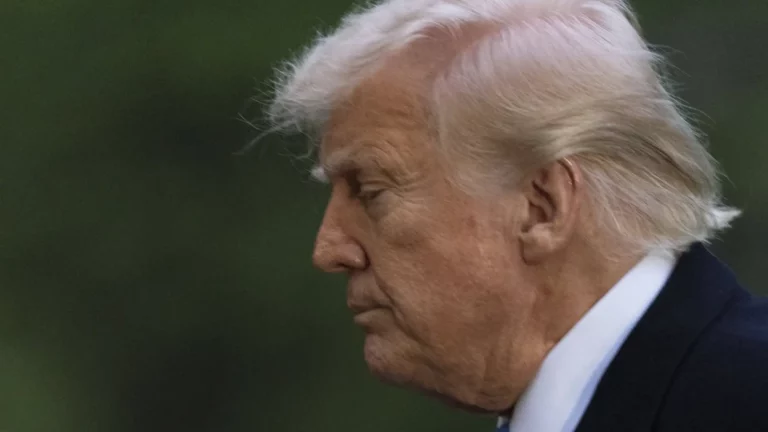
By – Samuel LopezFani Willis Blocked From Trump Fee Fight As Georgia Judge Lets $16.8 Million Reimbursement Battle Move Forward
INSIDE THIS REPORT A Georgia judge has ruled that Fulton County District Attorney Fani Willis cannot re-enter the collapsed Trump…
By – Samuel LopezFBI Bulletin Raises Troubling Questions About California’s Readiness
San Diego would rank high on any common-sense list because of its naval significance. Naval Base San Diego is a…
By – Samuel LopezCumulus Media Files for Chapter 11 as Radio Giant Moves to Cut Massive Debt
A Familiar Chapter in Cumulus’ Financial Story The bankruptcy marks the second time the broadcaster has sought court protection in…
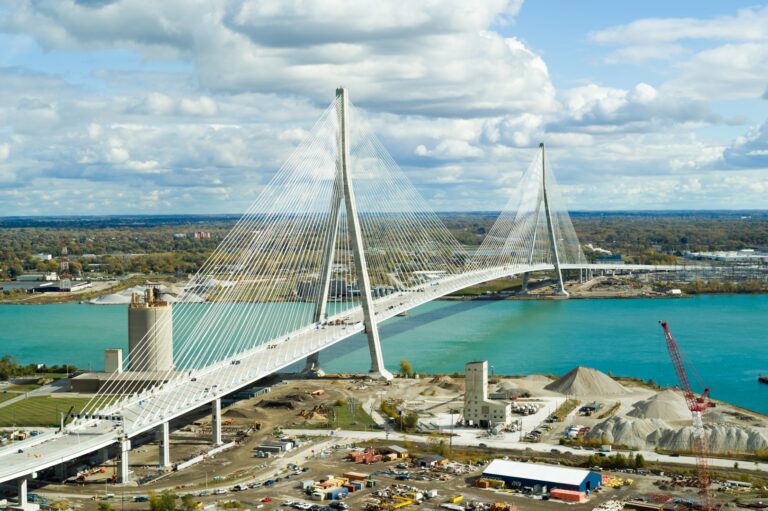
By – Rihem AkkoucheGordie Howe Bridge Tolls Revealed Ahead of Spring Opening
Local Residents React to Pricing Windsor resident Dariuss Piatkoeski said the newly announced rates strike the right balance. “I think…
By – Rihem AkkoucheGordie Howe Bridge Tolls Revealed Ahead of Spring Opening
Local Residents React to Pricing Windsor resident Dariuss Piatkoeski said the newly announced rates strike the right balance. “I think…
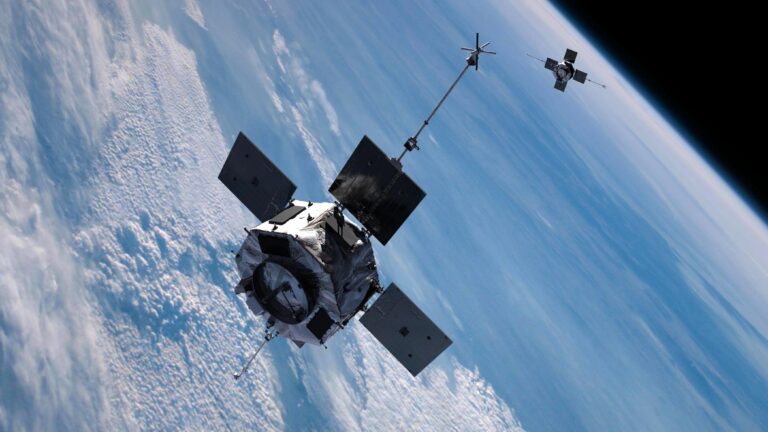
By – Rihem AkkoucheNasa Satellite to Crash to Earth as Spacecraft Re-enters Atmosphere
Meteor Strike in Germany Adds to Cosmic Drama The satellite’s predicted descent comes just days after another celestial surprise. On…
By – Rachel MooreLux Aeterna $10M Seed Funding Fuels Ambitious Reusable Satellite Vision
Hypersonic testing On-orbit computing In-space manufacturing The startup has also signed multiple partnerships with U.S. government organizations exploring reusable spacecraft…
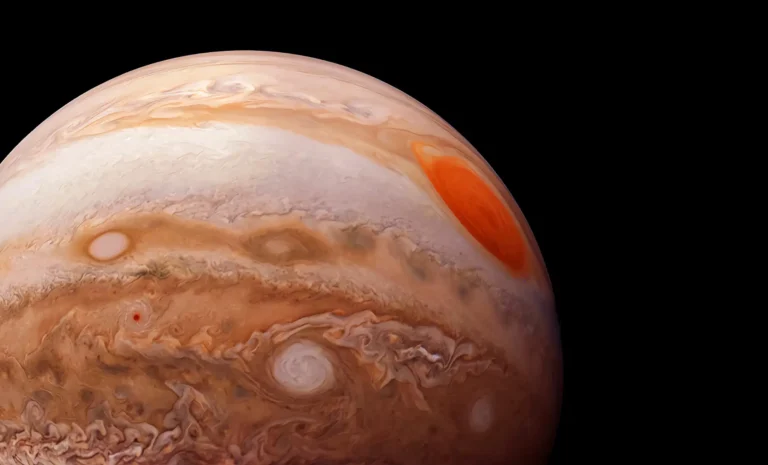
By – Rachel MooreJupiter’s Shift Direction Lights Up the Night Sky Again
A Reminder of the Solar System’s Dance For astronomers and backyard stargazers alike, Jupiter’s shift direction is another reminder that…
By – Rachel MooreGoogle and Tesla Power Grid Initiative Targets Lower Energy Costs
Tech Industry Promises to Address Costs Technology companies have recently begun pledging to help prevent those costs from falling on…
By – Rachel MooreMedtronic to Buy Scientia Vascular in $550 Million Neurovascular Deal
Leaders See Expanded Global Impact For Scientia, the acquisition opens the door to a much larger stage. “Scientia has developed…
By – Rachel MooreMedtronic to Buy Scientia Vascular in $550 Million Neurovascular Deal
Leaders See Expanded Global Impact For Scientia, the acquisition opens the door to a much larger stage. “Scientia has developed…
By – Rachel MooreWinklevoss Twins’ Bitcoin Transfer Sparks Market Speculation
Turbulence and Strategic Changes at Gemini The Winklevoss twins’ Bitcoin transfer also comes during a period of internal transition at…
By – Rihem AkkoucheAlabama Man Fatal Shooting Death Sentence Commuted by Governor
In a rare act of clemency that halted an imminent execution, the Alabama man fatal shooting death sentence tied to…
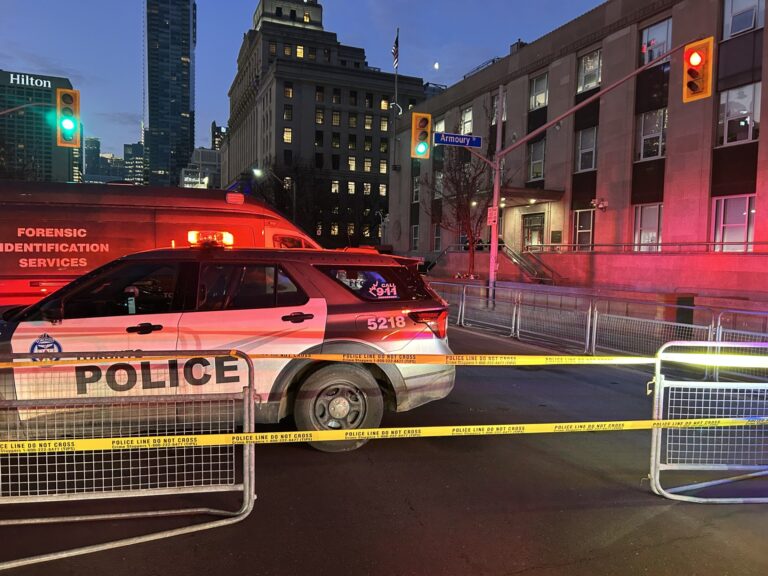
By – Rihem AkkoucheUS Consulate Shooting in Toronto Triggers National Security Investigation
Heightened Security Around Consulates Authorities said security will be strengthened around diplomatic buildings in the area, including both the U.S.…
By – Rihem AkkoucheExxonMobil to Move to Texas in Historic Corporate Shift
Governor Praises Corporate Move Texas Governor Greg Abbott welcomed the announcement, describing the state as fertile ground for major corporations.…
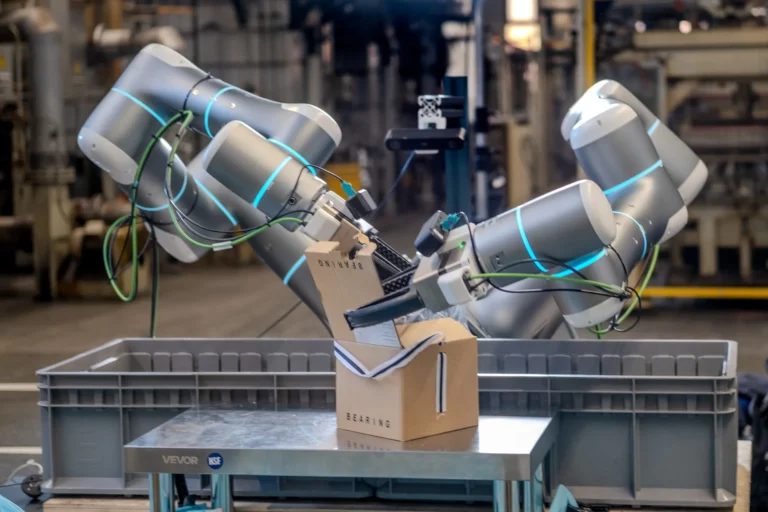
By – Rihem AkkoucheRhoda AI Secures $450M Funding to Power Next-Gen Industrial Robots
In a move set to electrify the robotics industry, Rhoda AI $450M funding marks one of the largest early-stage investments…
By – Rihem AkkoucheTrump’s Laser Talk Sparks New Questions About America’s Secret Arsenal
On the American side, the evidence also points to a military that is pushing hard into directed energy rather than…
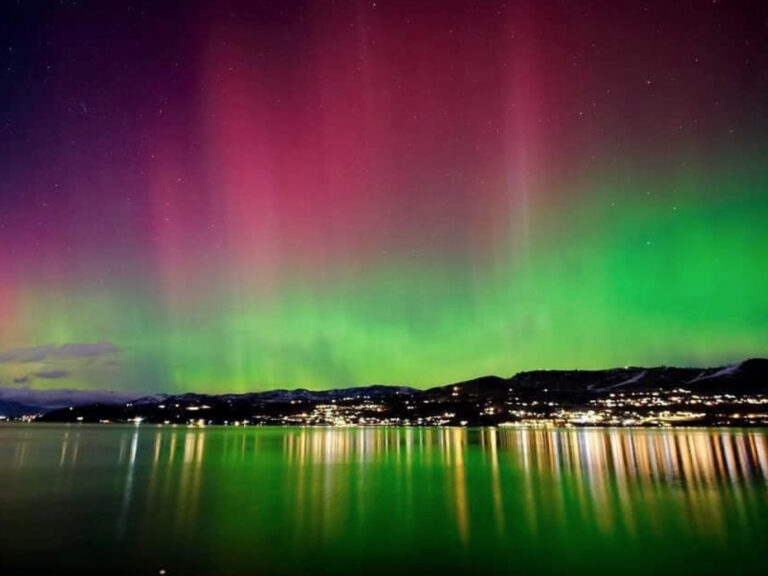
By – Samuel LopezThe Northern Lights Return
The Northern Lights have a chance to be visible from several northern U.S. states on Tuesday night, forecasters at the…
By – Jackie AllenFebruary Unemployment Up as Job Losses Surprise Economists
According to the BLS: Producer prices rose 2.9% year-over-year through January 2026 Core PPI increased 3.6%, excluding food and energy…
By – Jackie AllenLate-Night Attack by Venezuelan National at Florida Beach
Officials noted that the suspect had overstayed his work visa at the time of the attack. For more details on…
By – Jackie AllenTrump’s War in Iran: Congress Confronts Escalation After U.S. Strikes
On the Republican side, most lawmakers appear to back Trump’s strategy. Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Ark.), chair of the Senate Intelligence…
By – Jackie AllenU.S. And Israel Launch Major Strikes On Iran — What It Means For America
Continuation of military strikes if Iran persists in retaliatory attacks. Diplomacy or ceasefire negotiations if international pressure increases. A broader…
By – Samuel LopezRhoda AI Secures $450M Funding to Power Next-Gen Industrial Robots
In a move set to electrify the robotics industry, Rhoda AI $450M funding marks one of the largest early-stage investments…
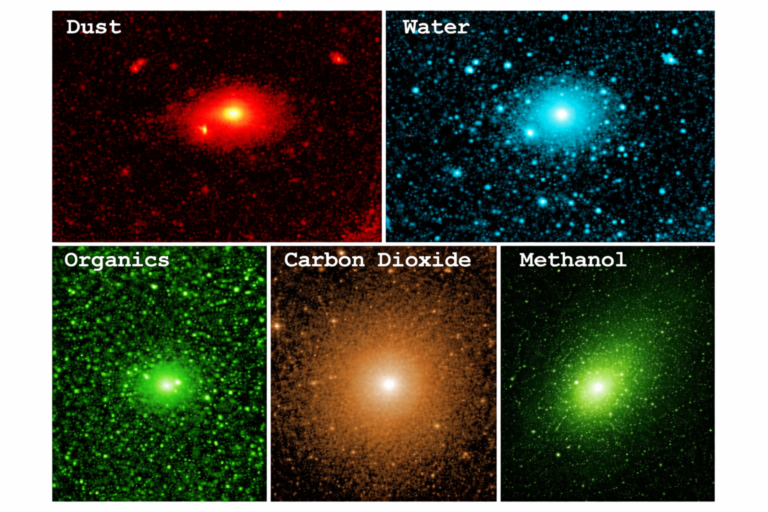
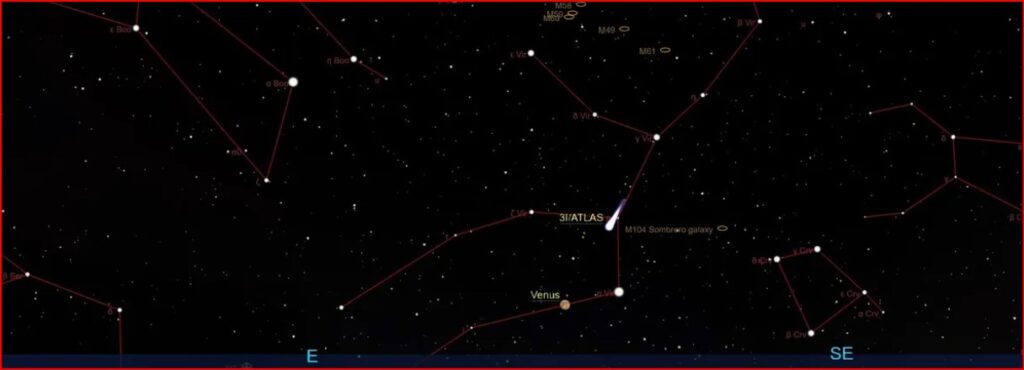
By – Rihem Akkouche3I/ATLAS Shocks Astronomers With Fuel-Like Methanol Molecule At Extraordinary Levels
The chemistry also appears more complex than a simple release from the nucleus alone. According to the ALMA findings, hydrogen…
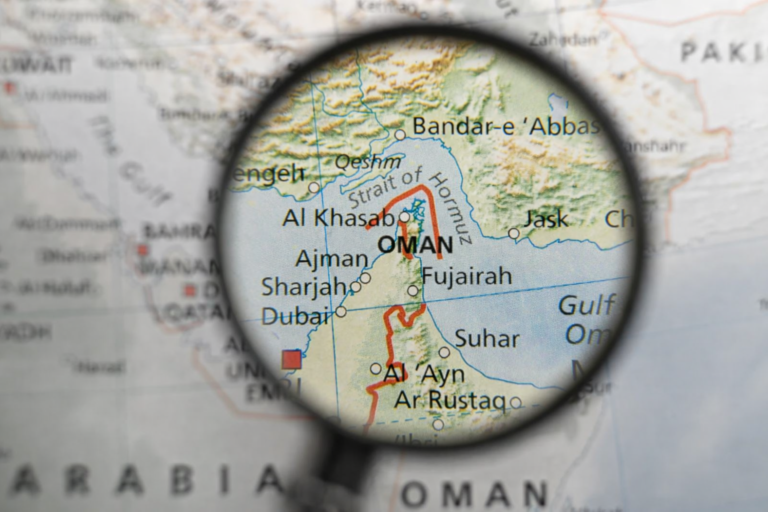
By – Samuel LopezWar Abroad, Risk At Home: Why Americans Are Quietly Reviewing Insurance Policies As Global Conflicts Expand
[USA HERALD] – As the United States confronts rising geopolitical tensions and the possibility of military engagement on multiple fronts…
By – Samuel LopezPentagon-Anthropic AI Dispute Explodes Into Federal Lawsuits Over AI Safety Policies
A Rare and Controversial Blacklist National security experts say the government’s designation is highly unusual. Supply-chain risk labels are typically…
By – Rachel MooreG7 Oil Reserve Release Considered as Iran War Disrupts Global Energy Supply
A Historic Supply Shock According to analysts at consulting firm Rapidan Energy Group, the closure of the strait has triggered…
By – Rihem AkkoucheOpenAI Acquires Promptfoo to Strengthen AI Security and Testing Tools
Recruiting the Minds Behind AI Infrastructure OpenAI has also strengthened its technical bench through high-profile hires. In February, the company…
By – Rihem AkkoucheWhen The Files Are Finally Unsealed The Most Mind-Bending Truth May Not Be What We Expect
[USA HERALD] – There is a widespread assumption that if governments release their most highly classified files related to unidentified…
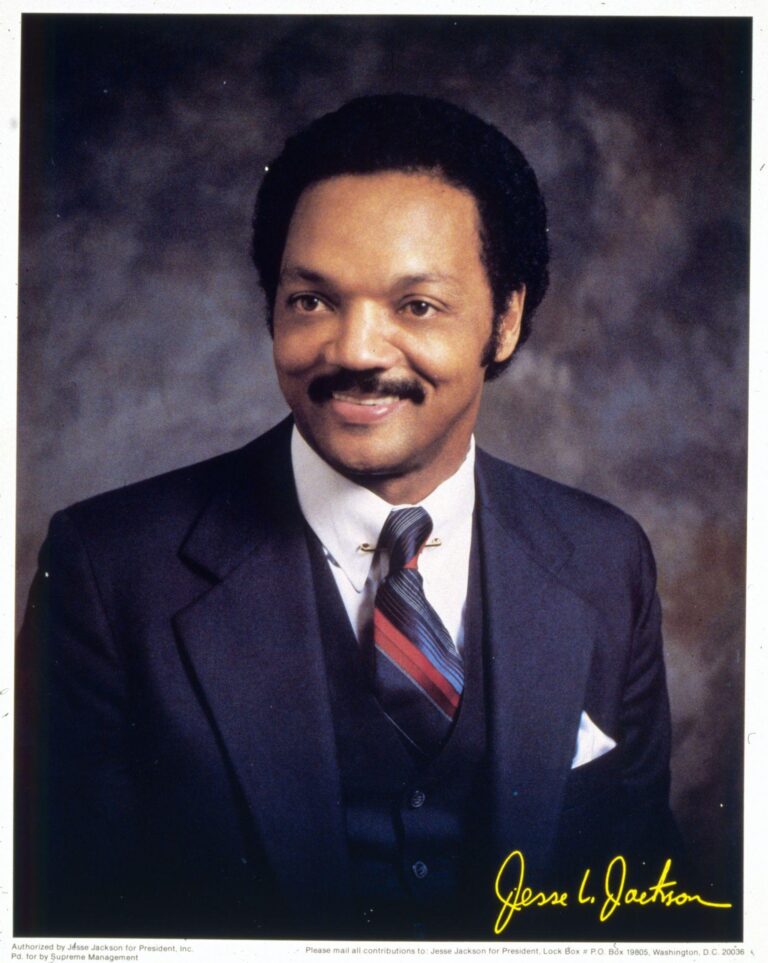
By – Samuel LopezCivil Rights Icon Rev. Jesse Jackson Dies at 84 As President Trump Issues Personal Tribute
Even in later years, as illness softened his voice and slowed his step, Jackson remained active. In 2021, he was…
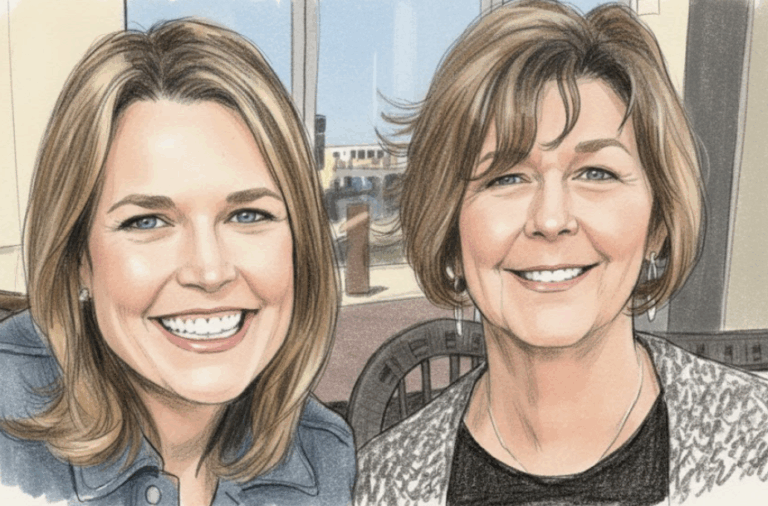
By – Samuel LopezClues to Savannah Guthrie Missing Mom’s Disappearance Found on Security System
Community Support Grows as Search Continues As the investigation intensifies, the local community has rallied around the family. Neighbors and…
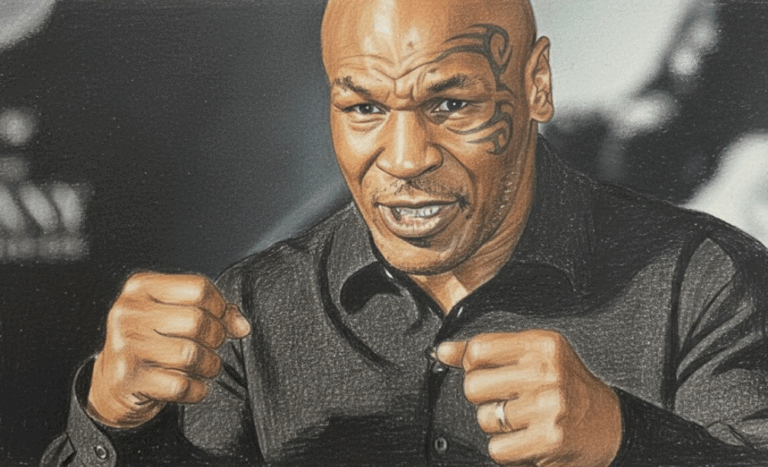
By – Jackie AllenMike Tyson Urges Americans to ‘Eat Real Food’ in Emotional Super Bowl Ad Highlighting Health Risks
Boxing legend Mike Tyson is using his platform ahead of Super Bowl 60 to address a personal and national health…
By – Tyler BrooksDeadly “Death Cap” Mushrooms in California Cause Multiple Deaths and Liver Transplants Amid Rare Super Bloom
California health officials are warning the public after four deaths and three liver transplants linked to the highly toxic death…
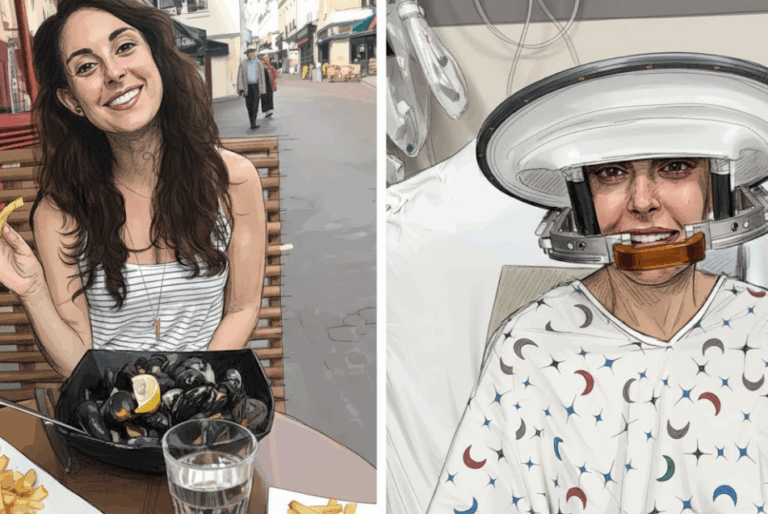
By – Ahmed BoughallebFrom Migraines to Miracles: How Becca Valle Survived a Glioblastoma Diagnosis Against the Odds
Becca Valle, 41, thought her headaches were just migraines—until a sudden, unbearable pain revealed something far more serious. In September…
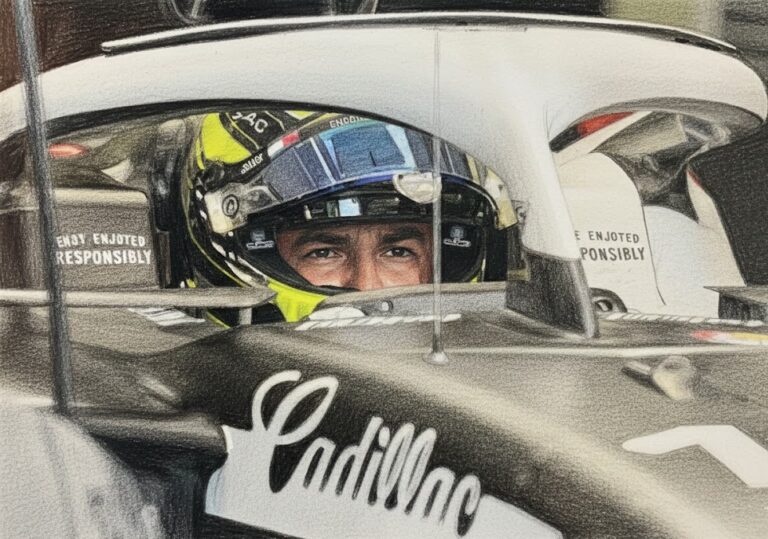
By – Tyler BrooksCadillac Names Inaugural Formula 1 Car MAC-26 in Tribute to Mario Andretti Ahead of 2026 Australian Grand Prix Debut
Lowdon has previously spoken about Andretti’s early encouragement during the team’s formation stages, noting that the racing legend asked him…
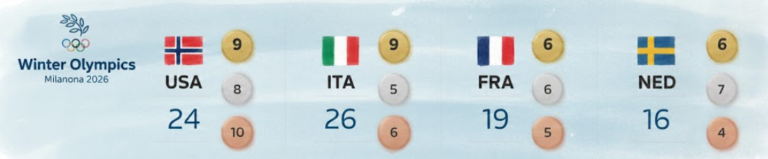
By – Ahmed BoughallebNorway Tops Medal Table After Day 13 at 2026 Winter Olympics as Team USA Surges Into Second Place
With 13 days complete at the 2026 Milan Cortina Winter Olympics, Norway sits atop the overall medal standings, collecting 34…
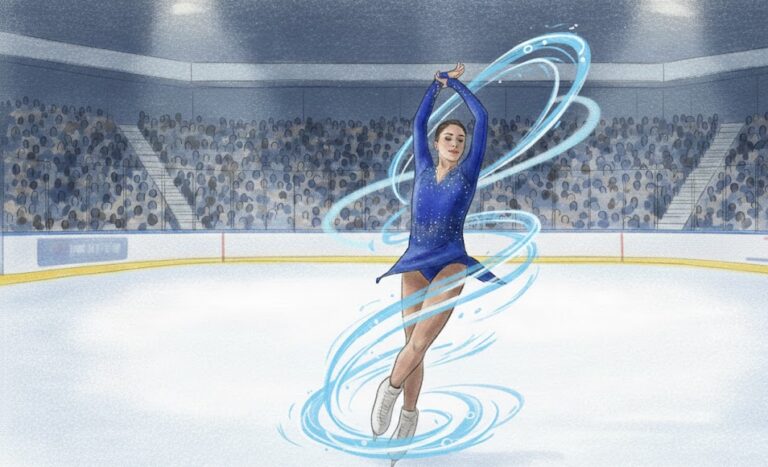
By – Ahmed BoughallebOlympic Science Explained: How Figure Skaters Spin at Blinding Speeds Without Getting Dizzy
When Amber Glenn finishes her routine, the arena usually rises with her. The music builds, her blades carve a tight…
By – Tyler BrooksOlympic Villages Run Out of Condoms at 2026 Milan-Cortina Games
Condom supplies in the Olympic Villages at the 2026 Winter Games have been temporarily depleted, the Milan-Cortina organizing committee confirmed,…
By – Tyler BrooksArizona Authorities Escalate Search for Savannah Guthrie’s Mom to a Criminal Investigation
USA TODAY’s live coverage: https://www.usatoday.com Pima County Sheriff’s Office: https://www.pimasheriff.org NBC News reporting: https://www.nbcnews.com As the investigation continues, officials say…
By – Jackie AllenThis early classification, however, sparked significant criticism. Advocates argue that placing aegosexuality in this category not only misunderstood the experience…
By – Jackie AllenNo posts found.
No posts found.
 No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!